The selection of materials in engineering and manufacturing hinges significantly on their mechanical properties, among which the "peek flexural modulus" stands out as a critical parameter. This metric indicates a material's stiffness when subjected to bending forces, serving as a pivotal factor in determining its suitability for a variety of applications, from aerospace components to medical devices. According to a report by the Materials Research Society, materials with high flexibility and strength, such as polyether ether ketone (PEEK), exhibit superior performance in demanding environments, which is largely attributed to their enhanced flexural modulus.
Dr. Elizabeth Carter, a leading expert in polymer engineering, notes, “Understanding the peek flexural modulus is essential for engineers to make informed decisions regarding material selection, especially in applications where mechanical stability is paramount.” Her insights underline the growing emphasis on advanced materials that can withstand thermal and mechanical stresses while maintaining their structural integrity. As industries evolve and push the boundaries of innovation, the importance of accurately measuring and interpreting the peek flexural modulus cannot be understated, ensuring that the right materials are employed to achieve optimal results in various applications.

The flexural modulus is a critical parameter in materials engineering, reflecting a material's ability to resist deformation under applied bending stress. It is defined as the ratio of stress to strain in a material subjected to a bending load within the elastic limit. Understanding this concept is essential for engineers and designers, as it aids in predicting how materials will behave when subjected to flexural forces, allowing for informed material selection based on specific application requirements.
When selecting a material for construction or manufacturing, the flexural modulus provides insight into the rigidity and stability of the material under load. A higher flexural modulus indicates a stiffer material, which is advantageous in applications where strength and resistance to bending are crucial. Conversely, materials with a lower flexural modulus may be preferred in applications requiring flexibility or shock absorption. By measuring the flexural modulus, engineers can better assess how different materials will perform in real-world scenarios, ultimately leading to safer and more efficient product designs.
This chart illustrates the flexural modulus values of various materials, which is crucial for material selection in engineering applications. Flexural modulus indicates the stiffness of a material when subjected to bending forces.
The Peak Flexural Modulus is a critical parameter in the realm of material selection as it directly relates to a material's ability to resist deformation under load. This property is particularly significant when dealing with structural components that experience bending forces. Understanding the Peak Flexural Modulus allows engineers and designers to predict how materials will perform in real-world applications, ensuring safety and longevity of the products being developed. By knowing the peak modulus, they can compare materials on the basis of their stiffness and performance, facilitating informed decisions that align with the requirements of various applications.
Moreover, the Peak Flexural Modulus plays a vital role in optimizing the balance between strength and weight. Materials with a high peak flexural modulus provide enhanced rigidity, which is essential for applications where maintaining form under stress is crucial. This is of paramount importance in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and construction, where the weight of materials must be minimized while still delivering maximum structural integrity. By emphasizing the significance of this property, designers can innovate and implement materials that not only meet performance standards but also contribute to greater efficiency and sustainability in their designs.
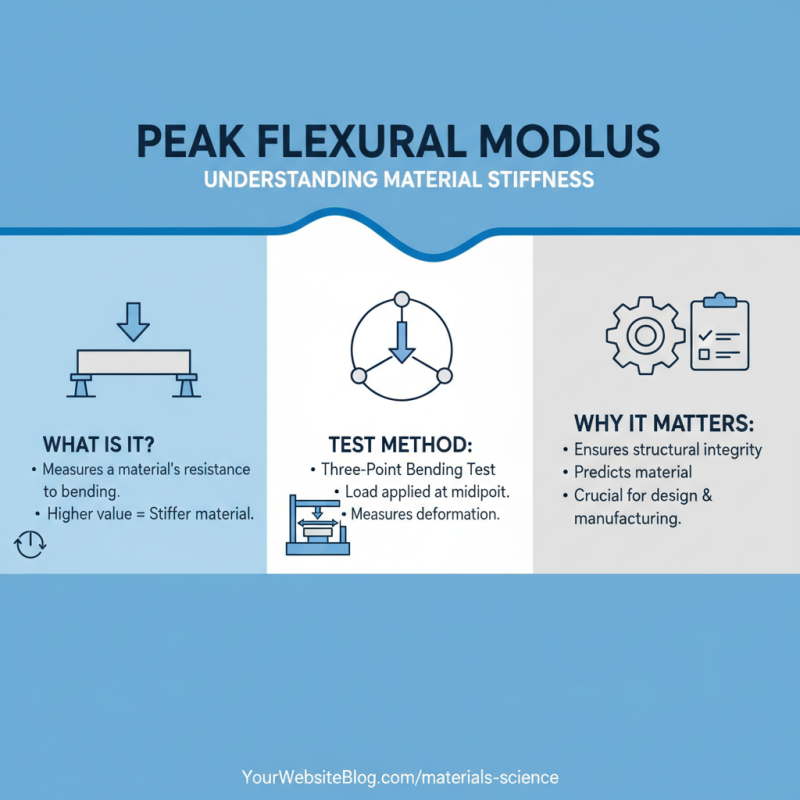
When selecting materials for construction or manufacturing, understanding the Peak Flexural Modulus is essential. This property measures a material's stiffness under bending stress, indicating how well it can withstand deformation. To accurately quantify this modulus, various testing methods and standards are available that ensure reliable results. The most common method is the three-point bending test, where a specimen is placed on two supports, and a load is applied at the midpoint until failure. This straightforward approach provides a clear measure of how much a material can flex without yielding.
Tips for performing flexural modulus tests include ensuring that specimens are prepared with precision to standard dimensions and maintaining consistent environmental conditions during testing, as temperature and humidity can affect results. Additionally, choose appropriate supports and loading rates to prevent premature failure of the sample during testing, which could lead to inaccurate readings.
Another crucial standard in the testing process is ASTM D790, which outlines methods for determining the flexural properties of various plastics. Following these established guidelines not only ensures consistency but also aids in the intercomparability of results across different materials. By adhering to recognized testing methods, engineers can make informed decisions about material selection that align with the desired performance criteria for their specific applications.
Understanding flexural modulus is crucial for selecting the right materials for different applications. The flexural modulus indicates a material's ability to resist deformation under load; thus, interpreting this data can help engineers and designers make informed choices. For instance, a high flexural modulus suggests that a material will maintain its shape under bending stress, making it suitable for structural components, while a lower modulus may be preferred for applications requiring flexibility.
When dealing with flexural modulus data, it's essential to consider how various factors, such as temperature and humidity, can affect the material's performance. For diverse applications, you should analyze not only the modulus value but also the testing conditions to ensure consistency across evaluations. This comprehensive approach helps avoid potential failures in real-world applications, ensuring that selected materials meet the specific demands of their intended use.
**Tips:** Always compare flexural modulus values within the same testing parameters to maintain consistency. It's also advisable to consider additional mechanical properties, such as tensile strength or impact resistance, when making your final material selection. Finally, conduct practical tests when possible to validate the theoretical data, as actual performance may differ due to environmental influences and processing techniques.
| Material Type | Flexural Modulus (GPa) | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) | 3.6 | Aerospace, Medical Devices |
| Polymer Composite (Carbon Fiber) | 10.0 | Automotive, Sporting Goods |
| Polypropylene (PP) | 1.5 | Packaging, Household Items |
| Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) | 2.5 | Construction, Pipes |
| Nylon 6,6 | 3.0 | Textiles, Automotive |

The peak flexural modulus is a crucial property in material selection, especially for applications requiring rigidity and resistance to deformation. Various materials exhibit differing peak flexural moduli, which can significantly influence decision-making in fields such as aerospace, automotive, and construction. Recent studies indicate that metals like steel can have peak flexural moduli upwards of 210 GPa, while polymers typically exhibit much lower values, ranging from 2 to 5 GPa. Composites often fall in between, with engineered composite materials showcasing peak flexural moduli around 30 GPa, demonstrating their potential in lightweight applications without compromising strength.
When comparing the peak flexural modulus across materials, it becomes evident that the molecular structure and processing methods substantially impact performance. For instance, thermosetting resins exhibit higher flexural strengths when compared with thermoplastics due to their cross-linked nature. The addition of fillers or reinforcements can enhance the flexural modulus of polymers, making them competitive with metals in certain contexts. This allows engineers to tailor materials to meet specific application needs while balancing weight and strength effectively.
Tips: Always consider the intended application and environmental factors when selecting materials. Use comparative data from reputable engineering sources to assess how different materials perform under expected load conditions. Additionally, testing prototypes can provide critical insights into how material selections will behave in real-world scenarios, ensuring optimal performance in your designs.