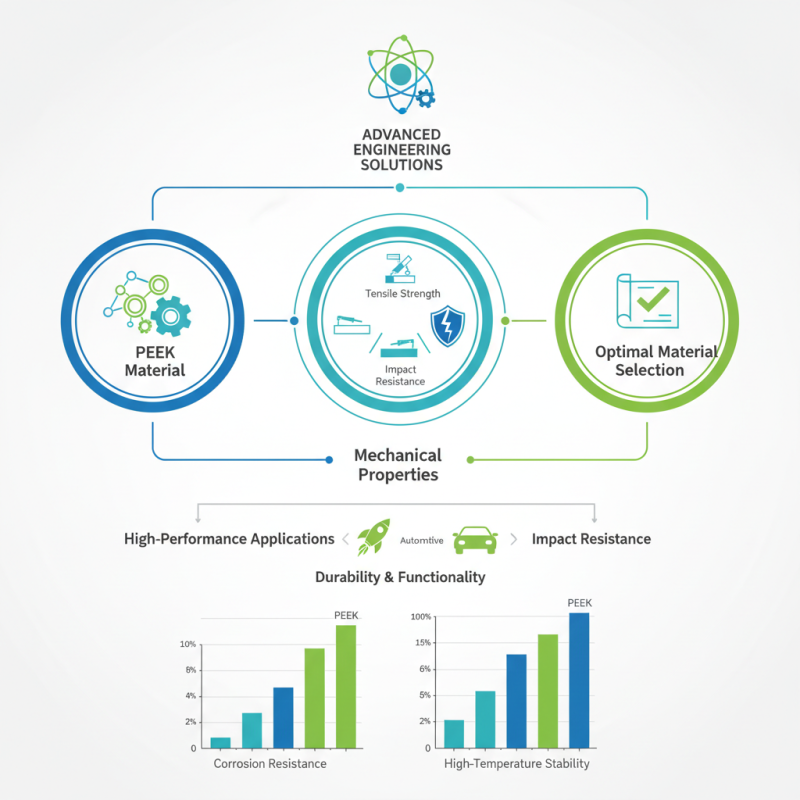
In the pursuit of advanced engineering solutions, the selection of materials plays a pivotal role in determining the performance and durability of components. Among the myriad of materials available, Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) stands out due to its exceptional mechanical properties, making it a top contender for high-performance applications. Understanding PEEK mechanical properties is crucial for engineers and designers aiming to optimize their material selection process. This introduction delves into the importance of thoroughly analyzing these properties, as they influence not only the structural integrity of the final product but also its functionality under varying operational conditions.
In recent years, the demand for lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and high-temperature-stable materials has surged. PEEK, with its unique blend of chemical resistance and thermal stability, has increasingly been adopted across industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical. However, to fully leverage the benefits of PEEK, a meticulous examination of its mechanical properties, including tensile strength, flexural modulus, and impact resistance, is essential. By comparing these properties with the specific requirements of intended applications, engineers can make informed decisions, ensuring optimal performance and longevity of their designs. This article will explore methodologies for analyzing PEEK mechanical properties and guiding strategies for effective material selection in engineering practice.
Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional mechanical properties, making it a preferred choice in various demanding applications. According to a report by Smithers Pira, PEEK exhibits a tensile strength of approximately 90 MPa and a flexural strength of around 170 MPa, indicating its capability to withstand rigorous stress conditions. These attributes are crucial in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical, where materials must perform reliably under extreme temperatures and pressures.
Additionally, the impact resistance of PEEK is noteworthy, with a notched Izod impact strength of around 4.5 kJ/m², which showcases its ability to absorb energy without fracturing. The thermal stability of PEEK, which can endure temperatures up to 260°C, makes it ideal for applications that require prolonged exposure to high temperatures. As highlighted in the "Thermoplastic Composites Market Report 2022," the demand for materials like PEEK is projected to grow significantly, driven by its unique combination of light weight, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength, poised to influence material selection strategies in the coming years.
| Property | Value | Unit | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 90 | MPa | Aerospace Components |
| Flexural Modulus | 3000 | MPa | Automotive Parts |
| Elongation at Break | 50 | % | Industrial Applications |
| Heat Deflection Temperature | 160 | °C | Electrical Insulation |
| Impact Strength | 50 | kJ/m² | Medical Devices |
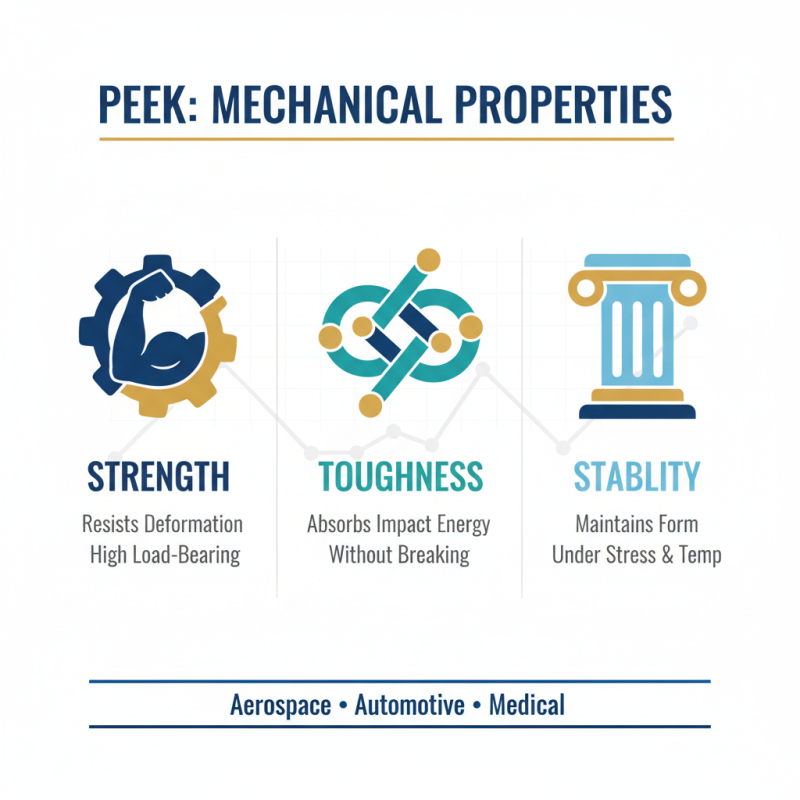
When analyzing the mechanical properties of PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone), three key characteristics stand out: strength, toughness, and stability. Strength refers to the material's ability to withstand force without deforming, making PEEK an exceptional choice for applications requiring high load-bearing capabilities. With its impressive tensile strength, PEEK can maintain structural integrity even under significant stress, which is crucial for industries like aerospace and automotive.
Toughness, on the other hand, encompasses the ability of PEEK to absorb energy and plastically deform without fracturing. This characteristic is essential for components that will experience impact loads, as it prevents sudden failures. PEEK’s toughness is particularly advantageous in manufacturing parts for medical devices and other dynamic environments, where reliability is paramount.
Lastly, stability is a vital property of PEEK, as it maintains its performance across a wide range of temperatures and environmental conditions. This thermal stability allows PEEK to be utilized in high-temperature applications where other materials might degrade. Together, these mechanical properties enable engineers and material scientists to make informed decisions when selecting PEEK for diverse applications, ensuring both performance and longevity.
When analyzing PEEK (polyether ether ketone) materials, utilizing the right techniques and tools is crucial for optimal material selection, especially in applications requiring high-performance components. One prevalent technique is differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), which measures the thermal properties of PEEK and can reveal important data regarding its melting and crystallization behaviors. This information is essential for predicting how the material will perform under different temperature conditions.
Another significant method is tensile testing, which assesses the material's mechanical properties, such as strength, elasticity, and elongation. These properties are critical for determining how PEEK will behave under stress in real-world applications. In addition to standard mechanical testing, advanced imaging techniques like scanning electron microscopy (SEM) can provide insights into the material's microstructure, helping engineers to understand failure mechanisms and the material’s durability. Combining these techniques allows for a comprehensive analysis, ensuring that the chosen PEEK material meets the specific requirements of the intended application.
When selecting materials for applications involving PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone), several factors come into play that influence the overall performance and suitability of the material. First and foremost, the mechanical properties of PEEK, such as tensile strength, flexural modulus, and impact resistance, need careful consideration. These attributes determine how well the material can withstand stress and strain under various environmental conditions. For industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical, where reliability is paramount, a thorough analysis of these properties is essential.
Another critical factor is thermal stability. PEEK's excellent resistance to heat makes it ideal for applications exposed to high temperatures; however, understanding the specific thermal limits and degradation characteristics under prolonged exposure is crucial. Additionally, the chemical resistance of PEEK against various solvents and acids is vital, especially in chemical processing and pharmaceutical applications. The presence of additives or reinforcements can enhance these properties, making it necessary to analyze not only the base material but also any composites or blends involved in the final product. Careful evaluation ensures optimal material selection that meets the demands of the specific application and environment.
This chart illustrates the mechanical properties of PEEK (Polyetheretherketone), which are crucial for optimal material selection in various applications. The properties highlighted include tensile strength, flexural strength, impact strength, and elastic modulus, providing insight into the performance and suitability of PEEK in demanding environments.
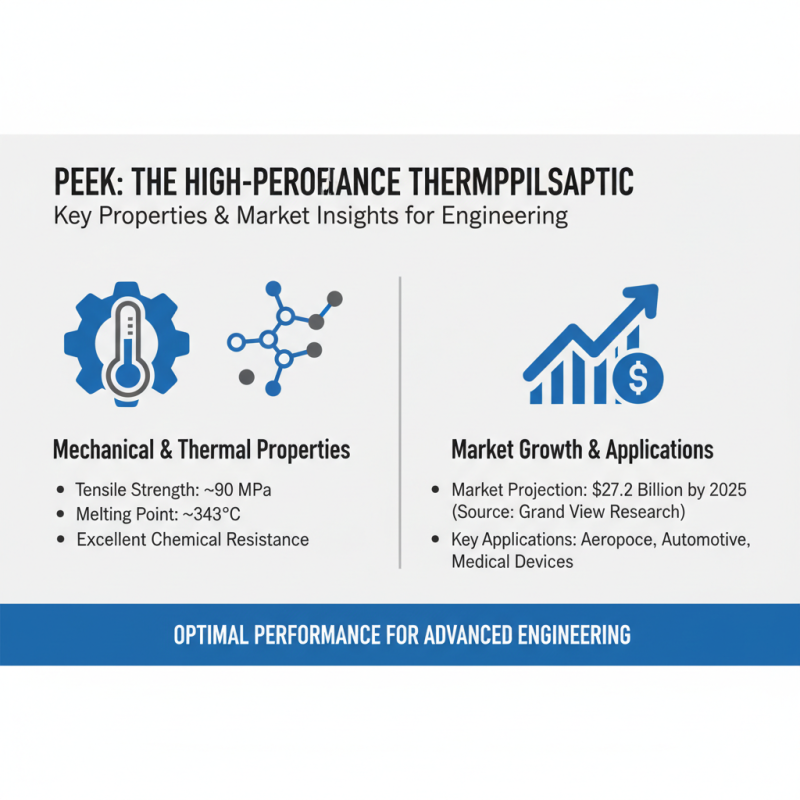
When selecting PEEK (Polyetheretherketone) for engineering projects, understanding its mechanical properties is crucial for achieving optimal performance in applications such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices. PEEK exhibits excellent tensile strength, with a typical value of around 90 MPa, and can withstand high temperatures, with a melting point of approximately 343°C. According to a recent market analysis by Grand View Research, the high-performance thermoplastics market is projected to reach $27.2 billion by 2025, largely influenced by increasing demand for PEEK in various advanced engineering applications.
To ensure the best use of PEEK, engineers should prioritize key mechanical properties such as thermal stability, chemical resistance, and impact strength. For example, its low coefficient of friction makes PEEK an ideal choice for bearings and seals in demanding environments. The International Journal of Engineering Research and Applications highlighted that incorporating specific fillers can further enhance PEEK’s properties; for instance, carbon fiber-reinforced PEEK shows improved rigidity and strength, making it suitable for components subjected to stringent mechanical loads. By applying these best practices and leveraging performance data, engineers can make informed decisions that maximize the reliability and efficiency of their projects involving PEEK.