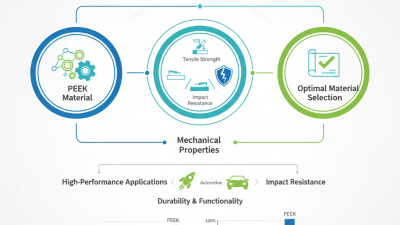
The optimization of PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) material composition is critical for maximizing performance in various industrial applications, particularly in sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and medical. As a high-performance engineering thermoplastic, PEEK offers exceptional chemical resistance, thermal stability, and mechanical properties, making it a material of choice for demanding environments. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global PEEK market is projected to reach USD 1.08 billion by 2026, driven by its increasing adoption in advanced manufacturing processes.
Analyzing the composition of PEEK materials is essential for understanding their behavior under different operational conditions. Studies have shown that varying the molecular weight and the ratio of comonomers can significantly influence mechanical strength, thermal resistance, and overall durability of PEEK products. Furthermore, industry benchmarks highlight that optimizing additives and fillers can enhance the performance characteristics of PEEK, ensuring compliance with stringent application requirements. This comprehensive understanding of peek material composition not only facilitates innovative product development but also supports effective material selection strategies, ultimately leading to improved operational efficiencies across various applications.

Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional strength and thermal stability, making it a material of choice in demanding applications such as aerospace, automotive, and medical sectors. Its unique properties stem from the aromatic backbone structure, which significantly enhances its rigidity and chemical resistance. According to a report by the global research firm, MarketsandMarkets, the PEEK market is projected to grow from USD 1.37 billion in 2020 to USD 2.36 billion by 2025, indicating a strong trend toward its adoption in high-performance environments.
PEEK exhibits a continuous service temperature of up to 260°C and retains mechanical properties even at elevated temperatures. Additionally, it has outstanding resistance to chemicals, including acids and bases, making it an ideal choice for components exposed to harsh environments. A study published in the Journal of Applied Polymer Science shows that PEEK can maintain more than 70% of its tensile strength after extended exposure to aggressive chemical agents. Moreover, its low coefficient of friction and high wear resistance underline its suitability for applications such as bearings and seals, where performance and longevity are critical.
The combination of these properties positions PEEK as a leader in advanced material compositions aimed at optimizing performance in specialized applications.
Analyzing the composition of PEEK (Polyether ether ketone) materials is integral for applications that demand high performance, particularly in industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical devices. Understanding the specific characteristics of PEEK and its additives can help in selecting the right material for particular applications. Key techniques include spectroscopy methods such as Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy. These techniques allow for precise identification of molecular structures and functional groups within the polymer, ensuring that the material's properties align with application requirements.
**Tip:** When utilizing FTIR, ensure that the sample preparation is consistent to achieve reliable results. Conduct multiple scans for accuracy and compare against reference spectra for better interpretation of the data.
Additionally, thermal analysis methods such as Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) and Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) provide insights into the thermal properties of PEEK materials. DSC can reveal information on melting points and glass transition temperatures, while TGA helps assess thermal stability and decomposition temperatures. This information is critical for applications subject to high temperature operations.
**Tip:** Implement a systematic approach when conducting thermal analysis, starting with TGA to determine the stability range, followed by DSC to explore the material’s thermal transitions. Providing a complete thermal profile is essential for evaluating performance under operating conditions.
| Test Method | Composition Element | Typical Percentage (%) | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| FTIR Spectroscopy | Carbon | 76 | Fundamental component of PEEK. |
| Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) | Oxygen | 22 | Important for thermal stability. |
| NMR Spectroscopy | Hydrogen | 2 | Influential in the polymer chain structure. |
| X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) | Sulfur | 0.5 | Contributes to chemical resistance. |
| Microscopy | Nitrogen | 0.5 | Affects polymer flexibility. |

When evaluating performance applications for PEEK (polyether ether ketone) materials, it is essential to consider their exceptional properties that set them apart in demanding environments. PEEK is recognized for its high temperature resistance, excellent chemical stability, and outstanding mechanical properties, making it suitable for various industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical. According to a report by Freedonia Group, PEEK's market is projected to grow by over 7% annually, driven by increased demand for lightweight and high-performance components.
In performance-critical applications, the ability to analyze the material composition of PEEK is vital. The glass transition temperature of PEEK is around 143°C (289°F), allowing it to maintain mechanical performance under extreme conditions. Additionally, it exhibits low creep under stress, which is vital in applications where dimensional stability is essential. By leveraging advanced analytical techniques like Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA) and Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC), engineers can optimize PEEK compositions tailored to specific applications, enhancing overall performance.
**Tips:** Always conduct a thorough evaluation of the specific environment in which PEEK will be used, considering factors such as temperature extremes, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress. Incorporating a proper design process and testing protocols can significantly reduce the risk of failure in high-performance applications. Additionally, exploring the impact of reinforcements, like carbon fibers or glass fibers, can further improve the material's performance characteristics, especially in load-bearing applications where stiffness and strength are critical.

When analyzing the performance of Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK) materials, several factors come into play that can significantly influence their effectiveness in various applications. The material's thermal stability, chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and wear performance are critical components that determine its suitability for specific environments. For instance, PEEK resists degradation from extreme temperatures, making it ideal for aerospace, automotive, and medical industries where high thermal resistance is essential.
One of the key tips for optimizing PEEK material performance is to consider the environment it will be exposed to. High humidity, exposure to harsh chemicals, or cyclic thermal loads can affect its longevity and functionality. Additionally, understanding the intended application will guide you in selecting the right grade of PEEK that aligns with your operational demands.
Another factor to consider is the method of processing PEEK. Techniques like injection molding and compression molding can alter the microstructure and properties of the material. Therefore, it’s crucial to select a processing method that aligns with the mechanical and thermal requirements of your specific applications. This consideration can maximize the benefits of PEEK's inherent properties while ensuring superior performance in demanding conditions.
When selecting and testing materials for applications involving
peek (polyether ether ketone), it is essential to focus on specific best practices that ensure
optimal performance. First and foremost,
thorough understanding of the application's demands is crucial. This includes evaluating factors such as
temperature resistance, chemical compatibility, and mechanical stress. Testing samples
under real-world conditions can provide insights into how the peek material will hold up over time, which is instrumental in avoiding
failures in demanding environments.
Another critical aspect is the method of material testing. Utilizing a variety of techniques, such as
tensile testing, thermal analysis, and chemical resistance testing, allows for a comprehensive
evaluation of peek's properties. It's also important to adhere to established industry
standards and protocols during testing to ensure the results are reliable and comparable. Such thorough testing and validation help in
selecting the right type of peek material tailored to specific performance needs, ultimately leading to
enhanced product reliability and longevity.